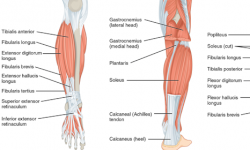
Bursitis is inflammation of a bursa. A bursa is a tiny fluid-filled sac that sits in large joints such as the shoulders, elbows, hips and knees and helps to reduce the friction between the joint and tendons as they move. Some of these joints may consist of more than one bursa.
Bursitis Causes
Repeated small stresses, overuse and sudden impact to the bursa can cause it to swell and become irritated. Other contributing factors may include; muscle weakness, muscular tightness, poor training technique, poor movement patterns and altered joint structure.
Sometimes the bursa can also become inflamed as a result of an infection or an underlying rheumatic condition.
Bursitis Signs & Symptoms
- Redness
- Swelling
- Tenderness on palpation
- Pain with movement of the affected joint.
Bursitis Diagnosis
After careful history taking and a physical examination your GP or physiotherapist will be able to diagnose if you have bursitis. Sometimes an ultrasound scan will be needed to confirm the diagnosis. The ultrasound scan will be able to show how severe the inflammation is and any associated impingement of the bursa in the joint. This will help with determining your prognosis.
Activities to avoid
- Shoulder bursitis; laying on the affected side, lifting, above shoulder height activities, putting your weight through your hands or elbows, holding the arm in a sustained position away from the side of your body, twisting of the arm.
- Hip bursitis; laying on the affected side, squatting, crossing your legs, running.
- Knee bursitis; kneeling, squatting, excessive stair climbing.
- Elbow bursitis; leaning on the elbow.
Bursitis can also occur in other areas such as the heel but the above areas tend to be the most common sites.
Bursitis Treatment
Conservative
Home management may consist of; Ice, rest, anti-inflammatories. Physiotherapy treatment may consist of the following:
- The therapist performing gentle range of movement exercises with the affected region
- Massage around the affected area
- Ultrasound
- Interferential therapy
- Home exercises to help strengthen or stretch the surrounding areas.
Invasive Management
Sometimes bursitis does not respond to conservative treatment and a cortisone injection maybe required. Subsequent cortisone injections maybe required if the bursitis does not respond to the first one, generally only a maximum of 3 cortisone injections are allowed in the one area.
It is often recommended to trial a period of conservative physiotherapy treatment first before heading down the ‘invasive’ road. If the bursitis does not respond to conservative treatment or the cortisone injection/or(s) then you maybe referred to an orthopaedic specialist. The orthopaedic specialist will review the affected area to determine whether surgery is needed.
Bursitis Prognosis
Typically bursitis, especially in the shoulder and hip, takes a lengthy period of time to resolve. This is because it often occurs in the joints that have to withstand a large amount of load and movement through them. You should expect to require regular physiotherapy treatment at first which may last between 3-6 months. Although progress is normally slow, if at all during this time your therapist does not think the affected area is responding like it should then they will send you to your GP for consultation about a cortisone injection or referral to a specialist.